Total Productive Maintenance
Maintenance has a far greater impact on corporate profitability than most managers are willing to consider, much less admit .And, as the competitive environment in the world continues to increase the pace, companies are looking for new strategies to save on costs, develop employees to face future challenges and bring about a new culture at work place. This has become imperative to stay in business and have an edge over the competition. In this situation, a number of strategies like Total Quality Management, Kaizen, quality circles, ISO certification, six sigma and Total productive Maintenance are available and it is the management choice to selectively implement these in their workplace.
What is TPM?
Seiichi Nakajima (1988) has defined TPM as an innovative approach to maintenance that optimizes equipment effectiveness, eliminates breakdowns, and promotes autonomous maintenance by operators through day-to-day activities involving the total work force. Thus,TPM is not a specific maintenance policy, it is a culture, a philosophy and a new attitude towards maintenance. The salient features of TPM is the involvement of operators in carrying out autonomous maintenance by participating in cleaning, lubrication, minor repair, adjustments etc. The benefits of TPM can be very tangible. There are organizations, which through implementation of TPM have been able to increase the production volume by 50%. Reducedown time by 27% and rate of defective products by 80%. In addition to tangible benefits, TPM also various intangible benefits such as fostering of teamwork, increase morale, safety and nurturing the work force increased intellectual capabilities having the potential of meeting today¢s level of competition and challenges.
Why TPM?
TPM was introduced to achieve the following objectives. The important ones are listed below.
- Avoid wastage in a quickly changing economic environment.
- Producing goods without reducing product quality.
- Reduce cost.
- Produce a low batch quantity at the earliest possible time.
EVOLUTION OF TPM
TPM descends from Japan and came into existence in the seventies. After Dr W Edward Deming made an impact in Japan through his teaching of quality, Japanese organization felt a need for autonomous maintenance and small group activities to support the quality movement. Today thousands of organizations all over the world are implementing TPM and about 100organisations are now doing it in India.
Total productive maintenance (TPM) is a proven strategy for medium to large industries to get superior business results and develop people skills to take on future business Challenges. Unlike ISO certification process, in TPM, focus is on maintaining the equipment and process in perfect condition- to get best quality products and involve all employees in Collectively carrying out loss elimination, using analytical problem solving tools.
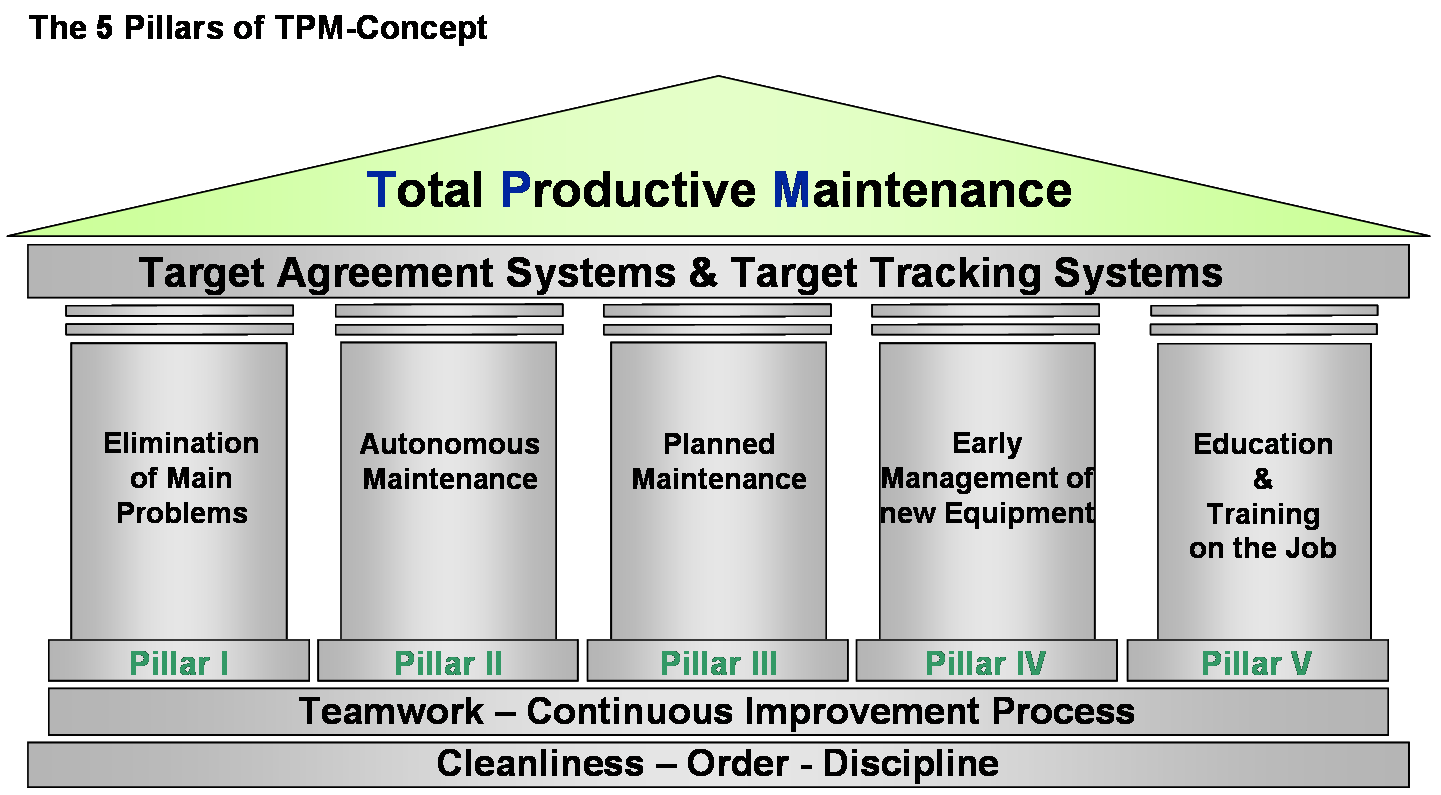
Objectives of Total Productive Maintenance
The main objective of TPM is to increase the Overall Equipment Effectiveness of plant equipment. TPM addresses the causes for accelerated deterioration while creating the correct environment between operators and equipment to create ownership.
OEE has three factors which are multiplied to give one measure called OEE
Performance x Availability x Quality = OEE
Each factor has two associated losses making 6 in total , these 6 losses are as follows:
Performance = (1) running at reduced speed - (2) Minor Stops
Availability = (3) Breakdowns - (4) Product changeover
Quality = (5) Startup rejects - (6) Running rejects
The objective finally is to identify then prioritize and eliminate the causes of the losses. This is done by self managing teams that problem solve. Employing consultants to create this culture is common practice.

